check
Use this for structured or unit testing.- Simple : small learning curve
- Practical : ways to de-clutter results
- Practical : results to screen or file
- Do we get an expected result?
- Is a variable a certain type or class?
- Does a call result in a particular exception?
include('check.php');
etc.
Start block...
check::StartBlock('First block');
... some tests
check::Is('Should be array','array',$someVar);
check::Test('Does it work',42,$universe->Answer());
check::Trap('Bad arg. excn.','arg','mult',null,'cat');
... more tests ...
check::EndBlock();
... more blocks of tests ...
check::Finish();
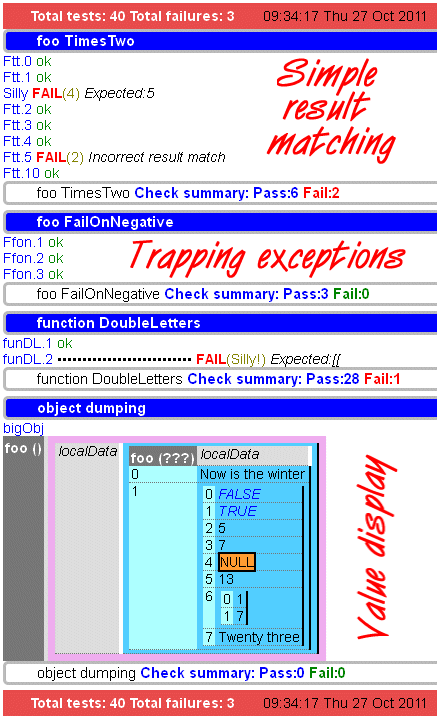 Example output
Example outputdump
Use this as much better version of print_r()- Simple : small learning curve
- Flexible : Trace execution, show stack
- Flexible : Tweakable display of complex objects
- Practical : results to screen or file
- Where are we in the code?
- Show a structured display of a variable including arrays and objects
- Show the stack including complex objects used as arguments
include('dump.php');
etc.
Immediate print...
print(dump::Value($object1),'What object 1 looks like');
... somewhere deeply nested
dump::Trace('STACK'); // will list complex arguments
... at a convenient place
dump::Output('someQuickFile.htm');
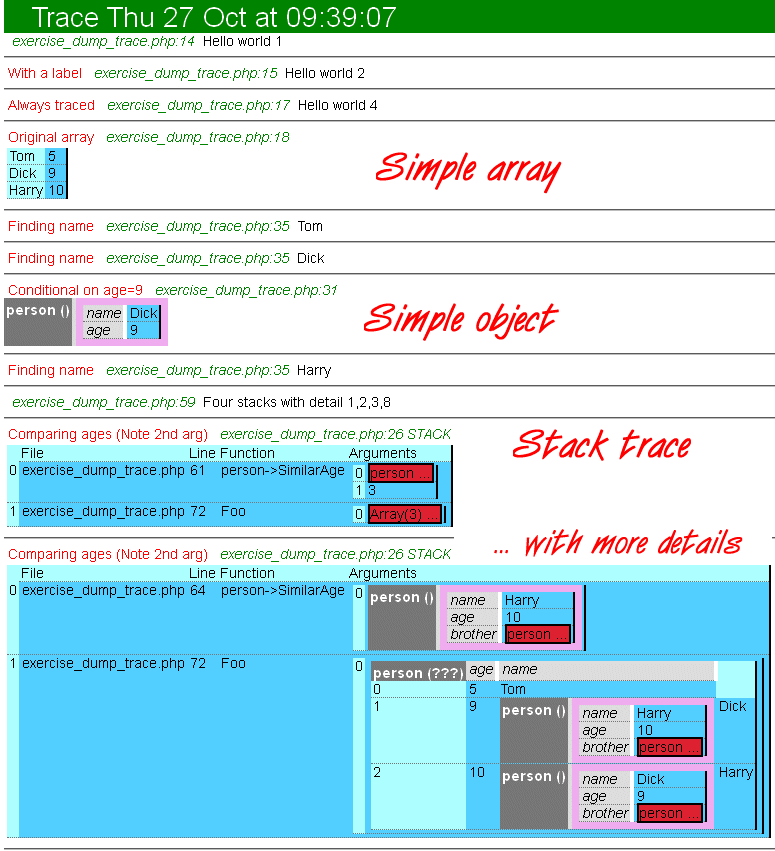 Example output
Example output